Introduction to Cairo’s LRT:
Cairo has recently introduced its Light Rail Transit (LRT) system, which is a significant step towards improving the city’s public transportation network. The LRT will connect important areas such as the New Administrative Capital and 10th of Ramadan City, making the commute more comfortable and convenient for residents and visitors. This modern rail system promises a faster and more efficient mode of transportation, which will help reduce congestion and improve urban mobility. Additionally, the LRT reflects Cairo’s commitment to sustainable and eco-friendly transit solutions. Overall, the LRT is a groundbreaking addition to Cairo’s transportation infrastructure, offering a transformative journey to its citizens.
What is LRT:
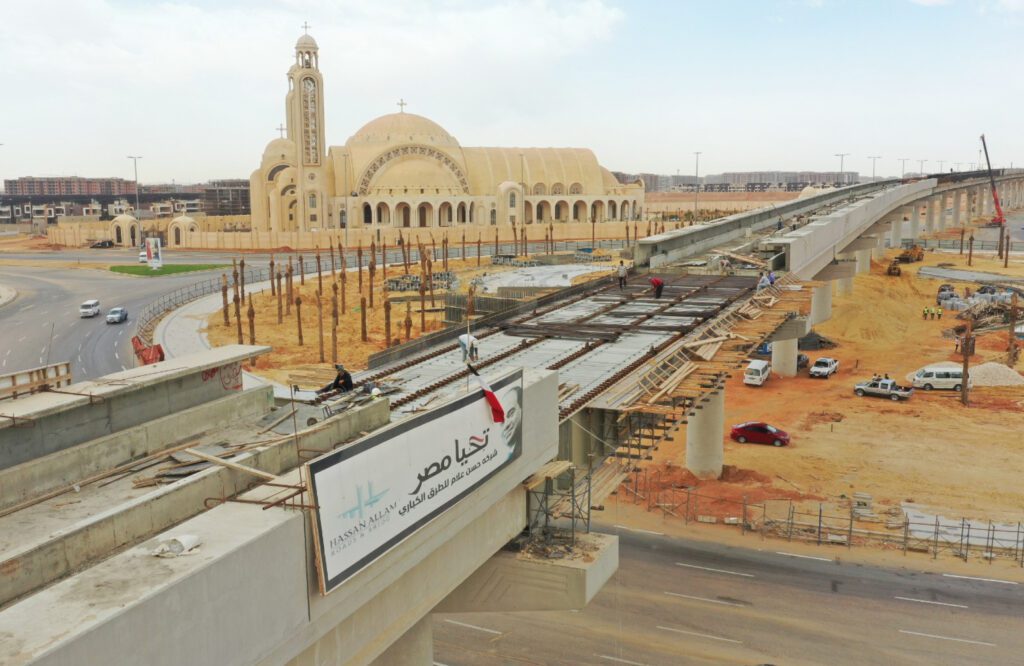

Light Rail Transit (LRT) is a medium-capacity public transport system that uses electrically powered rail cars, typically operating on exclusive rights-of-way. LRT is designed to be faster than traditional trams or streetcars, and it bridges the gap between heavy rail systems like subways and metros and local bus services. LRT systems can operate either in urban streets or on segregated tracks, and they are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency and lower environmental impact compared to other forms of urban transportation.
Technical Specifications and Design: Impressive numbers of LRT:
The Light Rail Transit (LRT) system in Cairo is an impressive project that will stretch over 103.3 km with 19 stations. The LRT is designed to accommodate 500,000 passengers per day and will operate over three phases. The 22 trains that will be used on the system have already been delivered at a total cost of $227 million and are designed to move at speeds of up to 120 km/hour. All stations on the system are configured to facilitate access and movement for people with disabilities, and they will include parking lots to encourage drivers of private cars to use the new system to alleviate congestion pressure on roads. The largest station on the LRT is the Adly Mansour interchange station in El-Salam City, which has an area of 1.1 million square metres. This station links the LRT, Cairo Metro’s third line, the Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system, Cairo-Suez railway line, and the SuperJet buses. The LRT will also intersect with the monorail at the new capital’s station of the Arts and Culture Centre and with Egypt’s first high-speed electric railway at an interchange station on Cairo-Sokhna highway. The duration of the trip from Adly Mansour to the New Administrative Capital will not exceed 45 minutes, and the LRT’s headway duration will be three to five minutes.
Executive Companies of LRT in Cairo:

The Cairo Light Rail Transit (LRT) project is a collaboration between local and international companies. Egyptian companies like The Arab Contractors and Orascom are working alongside international partners like Bombardier Transportation to complete the project’s civil works, which includes constructing bridges, tunnels, and stations. Chinese company Avic is responsible for the execution and manufacturing of the trains, as well as maintenance and spare parts. French company RATP Dev is in charge of managing and operating the rail. This partnership highlights the blend of local expertise and global standards in transport infrastructure. The involvement of these companies ensures that the Cairo LRT project is built to international standards and meets the needs of the city’s population, while also providing opportunities for local companies to participate in a major infrastructure project.
check out all the latest offers at Estatebook!
How big is the LRT projects:

The Cairo Light Rail Transit (LRT) project is a significant achievement of China’s railway technology exports to Africa. The project was jointly built by Chinese and Egyptian companies and is the first electrified LRT in Egypt and Africa. The project cost $1.24 billion and includes a line connecting Egypt’s New Administrative Capital with surrounding cities. In its first phase, the LRT has a daily transport capacity for 360,000 passengers, with 22 trains. This project is part of a series of Chinese railway projects in Africa, which highlights China’s significant role in developing infrastructure on the continent.
The Cairo LRT project is a comprehensive transit system with an estimated cost of around $35 billion. The civil works, which were carried out by construction companies, including the Arab Contractors and Orascom, as well as the Consortium of Bombardier Transportation, amounted to $530 million. Additionally, the cooperation between Egypt and Avic is valued at approximately $1.5 billion, while the collaboration with RATP Dev is valued at €183 million. The project’s cost highlights the significant investment required to build a modern and efficient transportation infrastructure, which can benefit the city in the long run.
Routes of LRT Cairo:
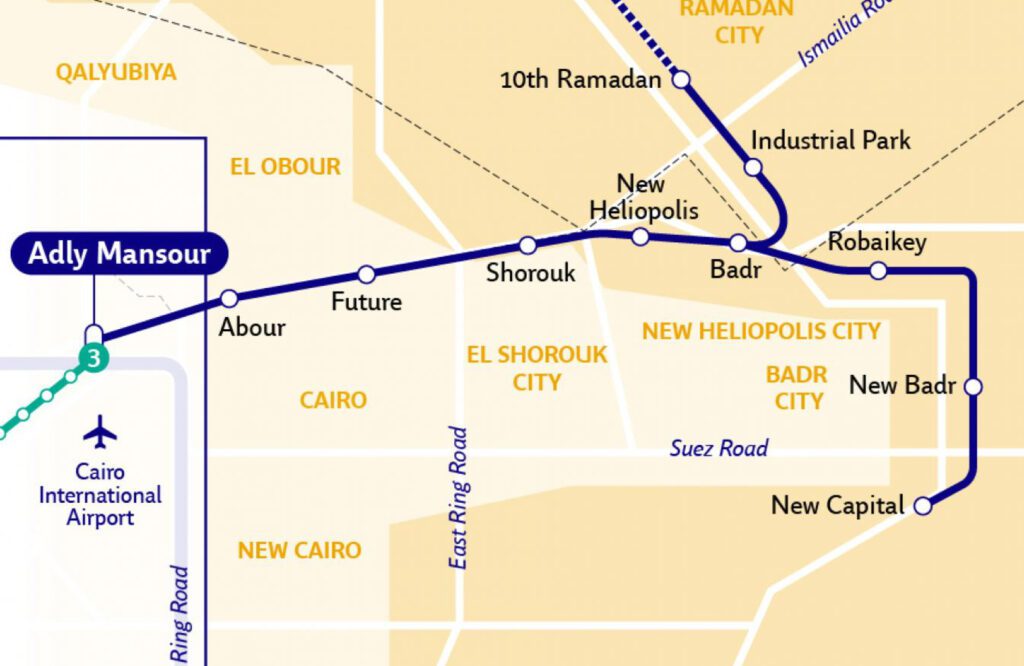
The Cairo LRT project is being implemented in multiple phases, each aimed at enhancing the system’s network and connectivity:
Phase 3: This phase of the project extends from the Christmas Cathedral station to the Central Capital Station, covering a distance of 20.4 km with four stations. This phase will provide a link to the Ain Sukhna/Matrouh high-speed train, further enhancing the system’s connectivity.
Phase 4: The fourth phase of the project was initiated in 2021 and aims to extend the LRT towards the 10th of Ramadan City, covering a distance of 16 km. This phase is crucial for connecting residents to the Administrative Capital and the Adly Mansour interchange station, integrating with the Greater Cairo Metro Line 3. The extension will further enhance the LRT’s network and provide a more comprehensive transportation system for the city’s residents and visitors.
How Much Will the LRT Ticket Be?
The pricing strategy for the Cairo LRT system is based on the number of stops. A ride lasting up to three stops costs EGP 15, and the price increases by EGP 5 with every additional three-stop increment. For a journey covering all 12 operational stations, the ticket price is EGP 35. This pricing structure is designed to cater to both short and long-distance travelers using the LRT services. The system aims to provide an affordable and efficient mode of transportation for Cairo’s residents and visitors, while also ensuring that the costs of operating the system are covered. With this pricing strategy, the LRT is accessible to a wide range of people, making it a popular choice for commuters in the city.
Mazar Mall in Sheikh Zayed: A Shopper’s Paradise
Future Prospects and Expansion Plans:

Phase 5 of the Cairo LRT project is currently under study. The proposed phase aims to extend from the Central Capital Station across the Cairo-Ain Sokhna Road to the Industrial Zone of the Administrative Capital. This 5.5 km extension includes one station. The implementation of this phase would further enhance the connectivity of the LRT system, providing access to key areas of the city and the Administrative Capital. However, it is worth noting that the implementation of this phase is still under study, and further details on its timeline and funding are yet to be released.
Conclusion and Reflection:

The introduction of the Light Rail Transit (LRT) system in Cairo marks the beginning of a transportation renaissance in the city. This marvel of engineering and urban planning is a testament to the city’s foresight, weaving together the past and future to offer a smoother, cleaner, and more efficient commute for its bustling population. With an impressive tapestry of routes and a promise to connect communities, the LRT is more than just a transit system; it’s Cairo’s leap towards a greener, more connected future.
As we reflect on the transformative power of the LRT, it becomes clear that this is just the beginning. Cairo’s journey towards sustainable urban mobility continues, and the LRT is its shining beacon. The LRT’s success will inspire more infrastructure projects that prioritize sustainable and eco-friendly transport solutions, paving the way for a brighter future for the city. The LRT system is a remarkable achievement that showcases the potential of collaboration and innovation in creating a better future for Cairo’s citizens.



